
The "fight or flight" response is a response that your body makes when stressed or anxious. Your body prepares you to confront or avoid danger when you are under Stress The stress reaction when used properly aids in our ability to overcome numerous obstacles. And yet problems arise when this reaction is frequently sparked by less significant everyday occurrences like financial difficulties, traffic congestion, employment concerns, or marital issues.
While feeling overwhelmed by stress or Anxiety, have you ever been instructed to take a Deep Breath? You may not have given it much attention, but this proverb raises an intriguing query: Does the mere act of controlling the breath provide respite from worried thoughts?
Anxiety is immediately apparent in your Breathing. One of the most well-known Yoga Teachings is found in the Bhagavad Gita, an epic text from India's Mahabharata. The protagonist of the Gita, Arjuna, is having an anxiety episode characterized by changes in his respiration, palpitations in his heart, and difficulty thinking. Though his teacher and mentor suggest practicing with breath, in the end understanding the nature of life ultimately helps him overcome his fear.
According to a study, a handful of brain cells are connected to breath and states of Mind. This emphasizes how slow breathing plays a role in reducing anxiety and calming the mind. Everyone has anxiety or stressful times when it may be difficult to maintain control regardless of age. The quickest approach to controlling your anger or other emotions in these situations is likely to practice deep breathing just like you would with therapeutic recreation. Anxiety, which is your body's response to stress, appears as an overwhelming fear or worry that is out of balance with the perceived threat.
Anxiety is common, but it can easily get out of hand and interfere with regular activities. It may cause you to harbor the deeply rooted belief that you aren't capable or that you are incapable of achieving certain objectives. When you feel uneasy about things, you can even distance yourself from those who you feel are helpful to you and to the situation in which you find yourself.
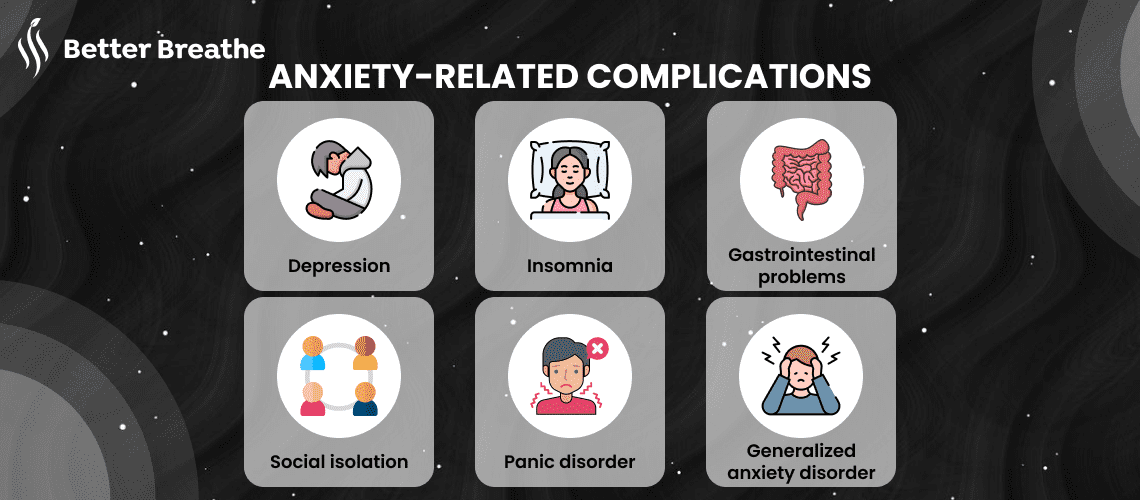
Untreated anxiety may eventually lead to an anxiety disorder. There are several typical anxiety disorders:
You are more likely to experience future Health Issues including diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease if you have an anxiety problem. Using natural methods such as controlled breathing may help you manage your Symptoms instead of relying solely on medicine. You can benefit from learning how to Breathe to Relax when you're in a stressful situation for the rest of your life. To assist you on your journey let's look at some safe breathing techniques.
Breathing Exercises take a short amount of time out of your day. There are various breathing exercises to select from, so choose one that works for you. These seven simple breathing techniques can be incorporated into your everyday practice to help you reduce anxiety.
Just behind the lungs, the diaphragm—a dome-shaped muscle—is used to breathe. This muscle is strengthened via Diaphragmatic Breathing, commonly referred to as belly breathing or abdominal breathing, which also fills the lungs with air.
Box Breathing, also known as square breathing, is a basic breathing technique that comprises inhaling, exhaling, and holding your breath.
The breath cycle should only last five seconds in order to practice Coordinated Breathing. This breathing pattern lowers blood pressure and pulse rate, soothing the nervous system.
As the name implies, this exercise involves breathing through a straw to lessen anxiety and stress. If you don't have a straw, you can pucker your lips on the exhale to perform the straw breathing exercise, which is also known as pursed lips breathing.
The three-part breath, commonly referred to as the yogic breath, is a wonderful grounding method that fills the full lungs. The abdomen, ribcage, and upper chest are referred to as the "three components of the breath".
In Sanskrit, Victory Breath is referred to as Ujjayi Breath. Because the sound produced by tightening the throat mimics waves crashing on the coast, it is also known as ocean breath.

To balance the flow of energy, Alternate Nostril Breathing, also called Nadi Shodhana in Sanskrit, entails breathing through just one nostril at a time. This breathing exercise calms the mind and the heart.
The Focus of our practice is to help you control persistent anxiety emotions and anxiety attacks that upset your stomach and heart. You'll feel considerably calmer if you make this exercise a regular part of your daily routine. Take some time to record your experiences with each of these seven breathing exercises after practicing them one at a time and deciding which ones you like. You can layer your preferred breathing techniques for deeper relaxation and relief from racing thoughts. Do you require more direction or are you prepared to advance your practice? Join us for a free session of Breathwork and meditation. Download our App on the Play Store and App Store.
Taking a breath is a natural thing: you Breathe In, you Breathe Out. Nothing complicated about it is there? But is there a proper method to breathe? Guess what? There are correct and incorrect techniques to obtain oxygen into your system through your lungs. According to our research, 90% of people only breathe at 50% of their maximum capacity. This indicates that many of us are not getting enough oxygen and blood flow.
Breathing may appear simple, yet there is a strategy for effective breathing. The most generally used term is Belly Breathing, although in technical terms it is Diaphragmatic breathing. Diaphragm breathing is a type of breathing that has been around for centuries, but its popularity has grown significantly in recent years due to its Health Benefits. Diaphragm breathing is a powerful tool to improve both physical and mental well-being. With the right technique, research has shown that diaphragm breathing can reduce blood pressure, improve cardiovascular health, and even regulate Stress and Anxiety levels.
You don't think about it much while you're breathing. It's just a natural subconscious process. If you're experiencing trouble breathing, you're probably performing a rather common error. You can diagnose your Breathing Problems by first looking at your respiratory system and what keeps it running.